When Can You Use Ideal Gas Law About Transcript The ideal gas law PV nRT relates the macroscopic properties of ideal gases An ideal gas is a gas in which the particles a do not attract or repel one another and b take up no space have no volume No gas is truly ideal but the ideal gas law does provide a good approximation of real gas behavior under many conditions
The ideal gas law also called the general gas equation is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions although it has several limitations What is its volume Solution The first step is to convert temperature to kelvins 34 273 307 K Now we can substitute the conditions into the ideal gas law The atm unit is in the numerator of both sides so it cancels On the right side of the equation the mol and K units appear in the numerator and the denominator so they cancel as well
When Can You Use Ideal Gas Law
 When Can You Use Ideal Gas Law
When Can You Use Ideal Gas Law
https://sciencenotes.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Real-Gas-vs-Ideal-Gas.png
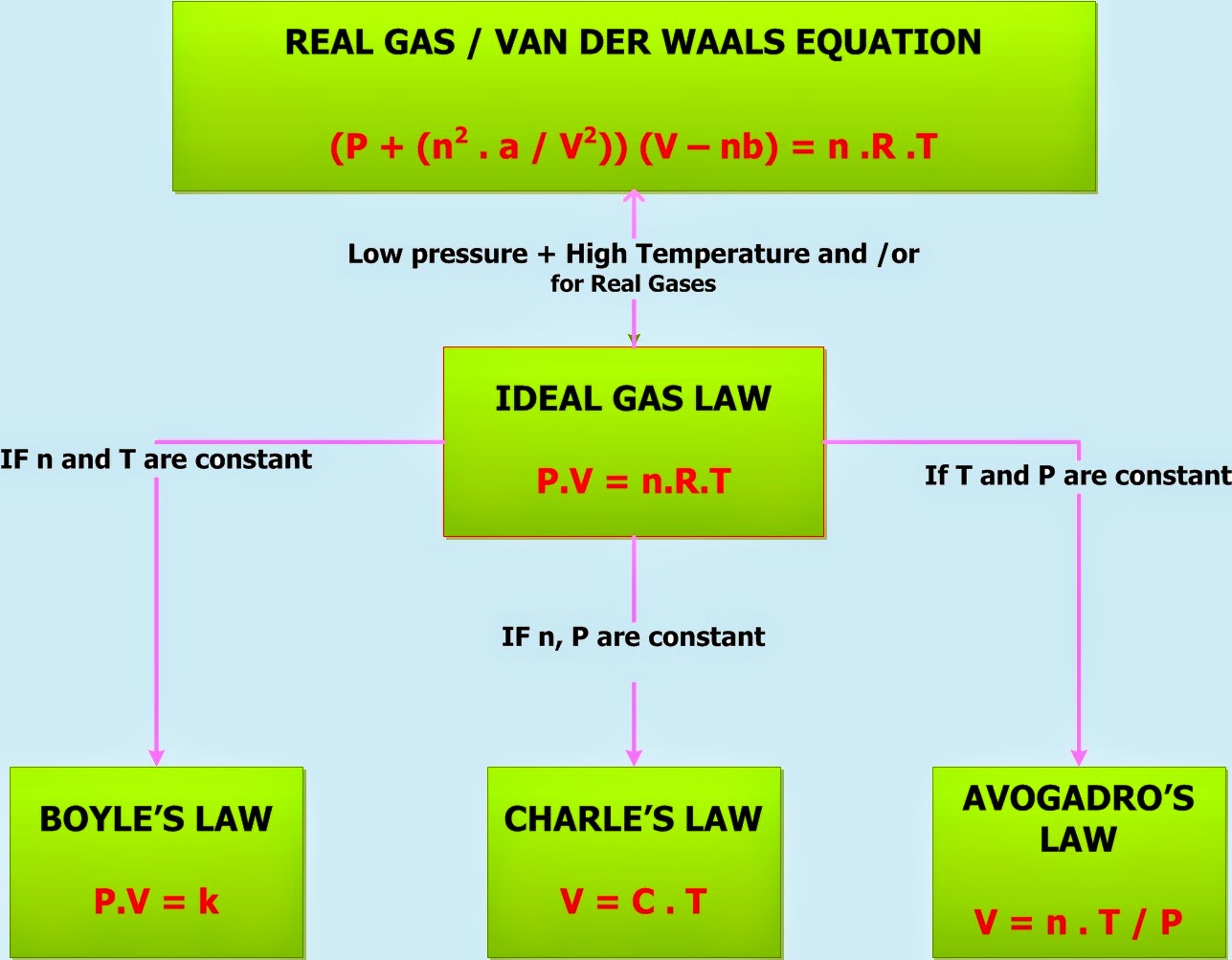
Category v t e An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions 1 The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law a simplified equation of state and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics
Templates are pre-designed files or files that can be utilized for various purposes. They can save effort and time by providing a ready-made format and design for developing different kinds of material. Templates can be utilized for personal or professional tasks, such as resumes, invites, leaflets, newsletters, reports, discussions, and more.
When Can You Use Ideal Gas Law

Ideal Gas Law And Applications

Formulas Used To Describe Gas Behavior

Teacher s Pet In Spanish The Ideal Gas Law Music History
R Values Ideal Gas Law Bar Gas Gas Law Constant It Is A Good

PPT The Ideal Gas Law PowerPoint Presentation Free Download ID 3608170
Ideal Gas Law R Values Ideal Gas Law Equation Formula Derivation

https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/can/CHEM_210%3A_General_Chemistry_I%2C_An_%22Atoms_Up%22_Approach/14%3A_Gases/14.03%3A_The_Ideal_Gas_Law
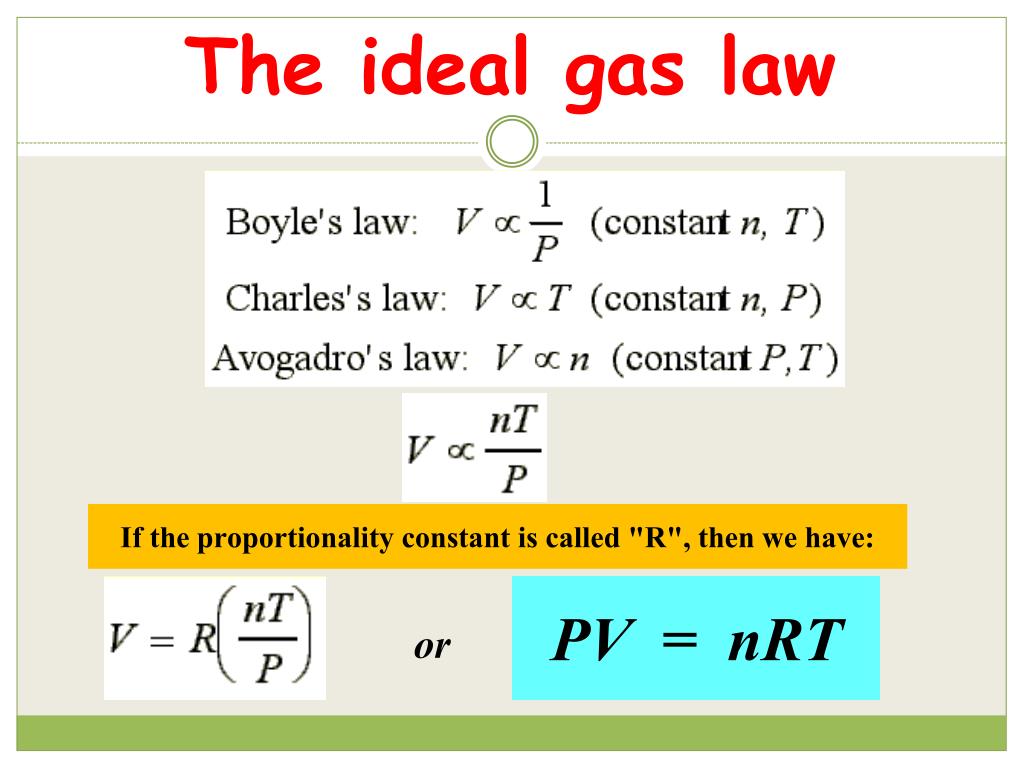
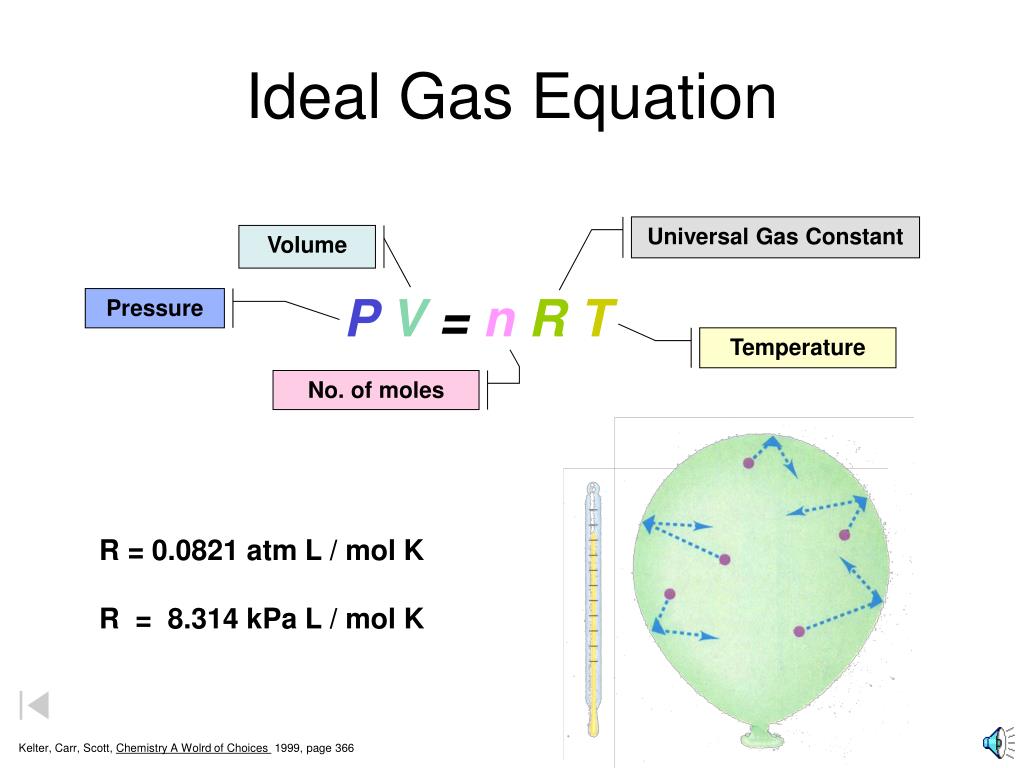
The ideal gas law PV nRT 6 3 1 6 3 1 P V n R T relates the pressure volume temperature and number of moles in a gas to each other R is a constant called the gas constant The ideal gas law is what is called an equation of state because it is a complete description of the gas s thermodynamic state
/GettyImages-1044456654-e456c93eeeaf46fe84cbeb0f95814fb6.jpg?w=186)
https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/can/intro/11:_Gases/11.09:_The_Ideal_Gas_Law:_Pressure_Volume_Temperature_and_Moles
The Ideal Gas Law is a single equation which relates the pressure volume temperature and number of moles of an ideal gas If we substitute in the variable R for the constant the equation becomes P V T n R The Ideal Gas Law is conveniently rearranged to look this way with the multiplication signs omitted P V n R T

https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry_Textbook_Maps/Supplemental_Modules_(Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry)/Physical_Properties_of_Matter/States_of_Matter/Properties_of_Gases/Gas_Laws/The_Ideal_Gas_Law
Step 2 Find the total moles of the mixed gases in order to use the Ideal Gas Equation ntotal nO2 nCl2 7 0 g O2 1 mol O2 32 00g O2 1 5 gCl2 1 mol Cl2 70 905 g Cl2 0 2188 mol O2 0 0212 mol Cl2 0 24 mol Step 3 Now that you have moles plug in your information in the Ideal Gas Equation

https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Map%3A_General_Chemistry_(Petrucci_et_al.)/06%3A_Gases/6.4%3A_Applications_of_the_Ideal_Gas_Equation
B Use the ideal gas law to determine the volume of O 2 required under the given conditions Be sure that all quantities are expressed in the appropriate units Solution mass of H 2 SO 4 moles H 2 SO 4 moles O 2 liters O 2 A We begin by calculating the number of moles of H 2 SO 4 in 1 00 ton
https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Book%3A_General_Chemistry%3A_Principles_Patterns_and_Applications_(Averill)/10%3A_Gases/10.03%3A_The_Ideal_Gas_Law
The ideal gas law PV nRT 10 3 1 10 3 1 P V n R T relates the pressure volume temperature and number of moles in a gas to each other R is a constant called the gas constant The ideal gas law is what is called an equation of state because it is a complete description of the gas s thermodynamic state
Also called perfect gas law gas laws ideal gas law relation between the pressure P volume V and temperature T of a gas in the limit of low pressures and high temperatures such that the molecules of the gas move almost independently of each other In such a case all gases obey an equation of state known as the ideal gas law PV nRT The Ideal Gas Law is one of the Equations of State Although the law describes the behavior of an ideal gas the equation is applicable to real gases under many conditions so it is a useful equation to learn to use The Ideal Gas Law may be expressed as PV NkT where P absolute pressure in atmospheres V volume usually in liters
The ideal gas law describes the behavior of an ideal gas a hypothetical substance whose behavior can be explained quantitatively by the ideal gas law and the kinetic molecular theory of gases Standard temperature and pressure STP is 0 C and 1 atm The volume of 1 mol of an ideal gas at STP is 22 41 L the standard molar volume All of the