When To Use Ideal Gas Law Use the ideal gas law to calculate pressure change temperature change volume change or the number of molecules or moles in a given volume Use Avogadro s number to convert between number of molecules and number of moles Figure 13 16 The air inside this hot air balloon flying over Putrajaya Malaysia is hotter than the ambient air As a
The ideal gas law can also be used to determine the density of gases Density recall is defined as the mass of a substance divided by its volume d m V 6 6 1 6 6 1 d m V Assume that you have exactly 1 mol of a gas If you know the identity of the gas you can determine the molar mass of the substance The ideal gas law is derived from empirical relationships among the pressure the volume the temperature and the number of moles of a gas it can be used to calculate any of the four properties if the other three are known Ideal gas equation PV nRT where R 0 08206L atm K mol 8 3145 J K mol
When To Use Ideal Gas Law
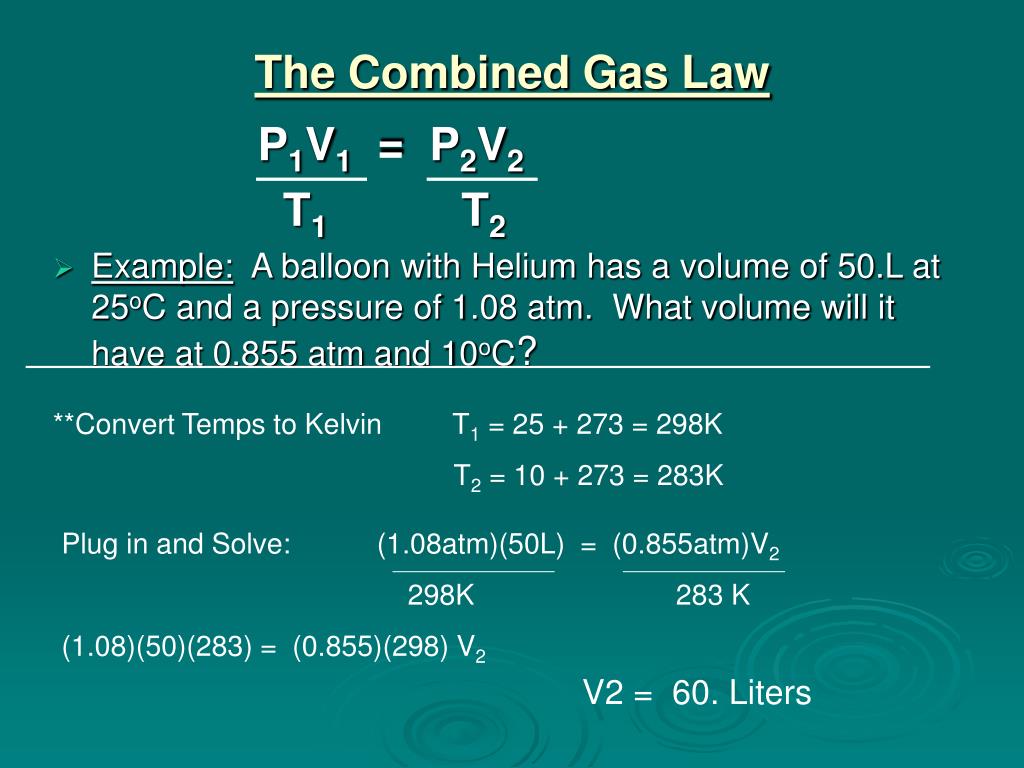 When To Use Ideal Gas Law
When To Use Ideal Gas Law
https://image2.slideserve.com/5321509/the-combined-gas-law-l.jpg
B Use the ideal gas law to determine the volume of O 2 required under the given conditions Be sure that all quantities are expressed in the appropriate units Solution mass of H 2 SO 4 moles H 2 SO 4 moles O 2 liters O 2 A We begin by calculating the number of moles of H 2 SO 4 in 1 00 ton
Templates are pre-designed files or files that can be used for different functions. They can save time and effort by providing a ready-made format and layout for producing various type of content. Templates can be used for individual or expert tasks, such as resumes, invites, leaflets, newsletters, reports, presentations, and more.
When To Use Ideal Gas Law

Ideal Gas Law Definition Formula Facts Britannica

Combined Gas Law Worksheet Answers

Ideal Gas Law And Applications
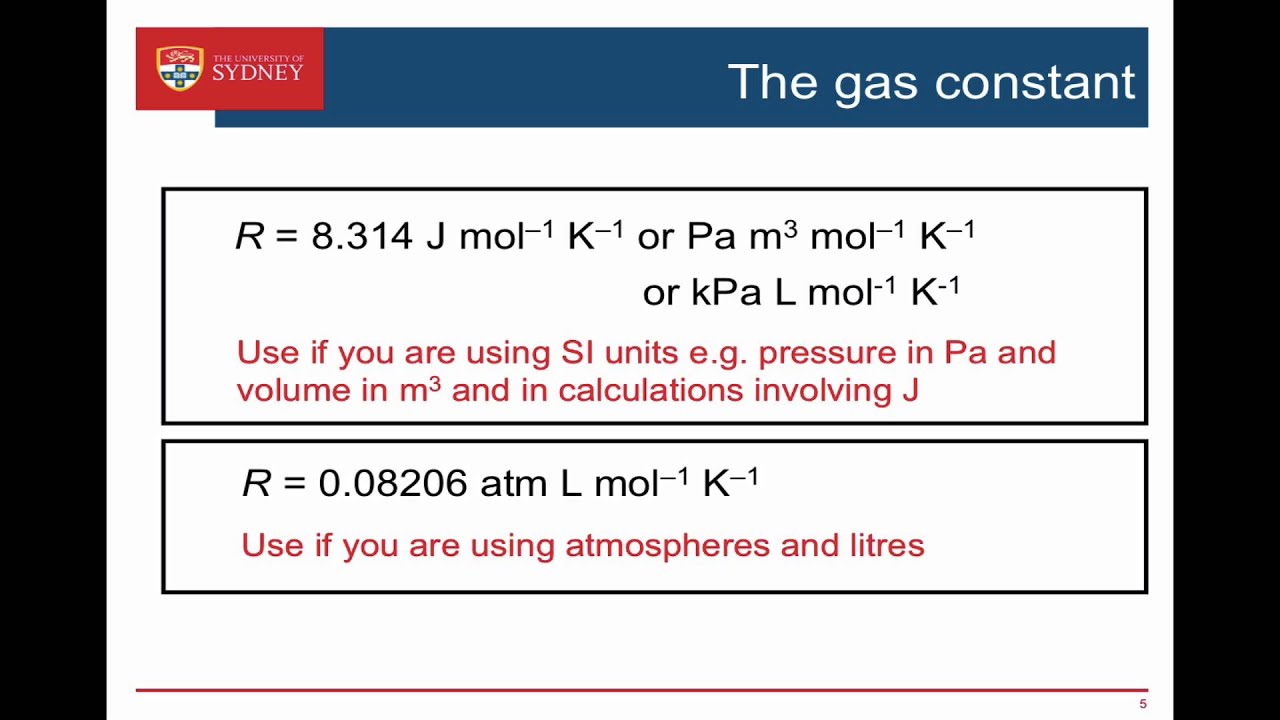
Ideal Gas Law Constant R Values The Ideal Gas Equation The Constant

Gas What Is The Ideal Gas Law
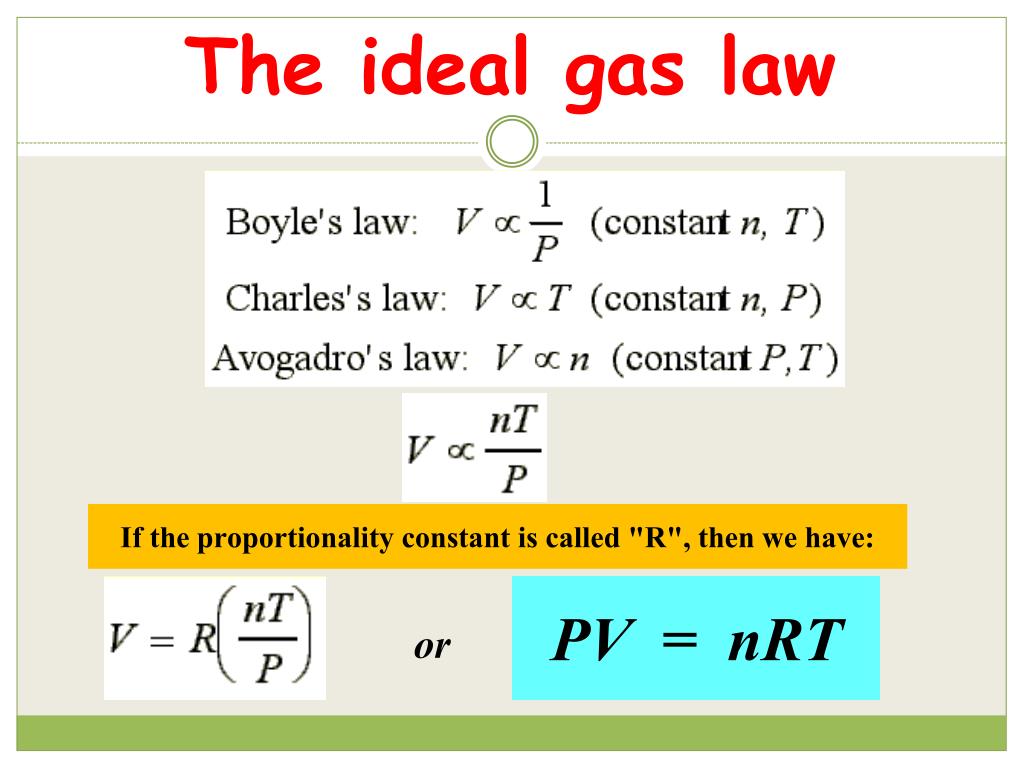
R Values Ideal Gas Law Bar Gas Gas Law Constant It Is A Good

https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/thermodynamics/temp-kinetic-theory-ideal-gas-law/a/what-is-the-ideal-gas-law
The term ideal gas refers to a hypothetical gas composed of molecules which follow a few rules Ideal gas molecules do not attract or repel each other The only interaction between ideal gas molecules would be an elastic collision upon impact with each other or an elastic collision with the walls of the container What is an elastic collision
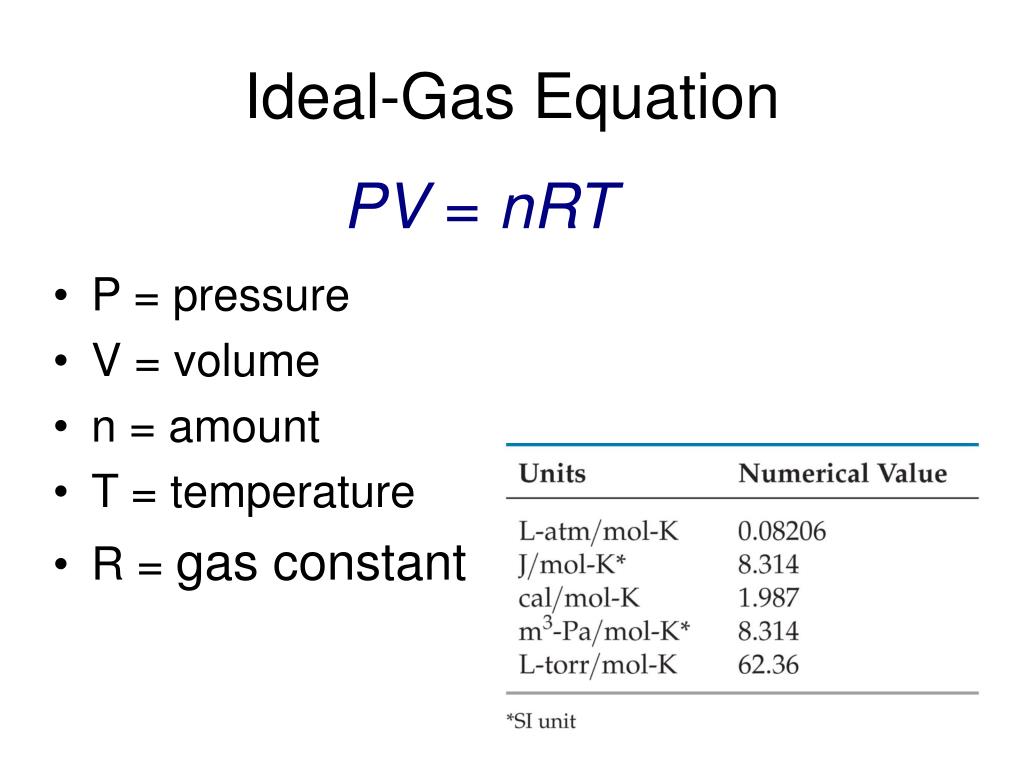
https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry_Textbook_Maps/Supplemental_Modules_(Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry)/Physical_Properties_of_Matter/States_of_Matter/Properties_of_Gases/Gas_Laws/The_Ideal_Gas_Law
The Ideal Gas Equation Before we look at the Ideal Gas Equation let us state the four gas variables and one constant for a better understanding The four gas variables are pressure P volume V number of mole of gas n and temperature T Lastly the constant in the equation shown below is R known as the the gas constant which will be discussed in depth further later

https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Book%3A_General_Chemistry%3A_Principles_Patterns_and_Applications_(Averill)/10%3A_Gases/10.03%3A_The_Ideal_Gas_Law
The ideal gas law PV nRT 10 3 1 10 3 1 P V n R T relates the pressure volume temperature and number of moles in a gas to each other R is a constant called the gas constant The ideal gas law is what is called an equation of state because it is a complete description of the gas s thermodynamic state

https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/can/intro/11:_Gases/11.09:_The_Ideal_Gas_Law:_Pressure_Volume_Temperature_and_Moles
The Ideal Gas Law is a single equation which relates the pressure volume temperature and number of moles of an ideal gas If we substitute in the variable R for the constant the equation becomes P V T n R The Ideal Gas Law is conveniently rearranged to look this way with the multiplication signs omitted P V n R T
/GettyImages-1044456654-e456c93eeeaf46fe84cbeb0f95814fb6.jpg?w=186)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ideal_gas_law
Equation Molecular collisions within a closed container a propane tank are shown right The arrows represent the random motions and collisions of these molecules The pressure and temperature of the gas are directly proportional As temperature increases the pressure of the propane gas increases by the same factor
In such a case all gases obey an equation of state known as the ideal gas law PV nRT where n is the number of moles of the gas and R is the universal or perfect gas constant 8 31446261815324 joules per kelvin per mole The universal gas constant is defined as Avogadro s number NA times the Boltzmann constant k Gas Laws Overview Page ID Created in the early 17th century the gas laws have been around to assist scientists in finding volumes amount pressures and temperature when coming to matters of gas
An ideal gas contains molecules of a negligible size that have an average molar kinetic energy that depends only on temperature Intermolecular forces and molecular size are not considered by the Ideal Gas Law The Ideal Gas Law applies best to monoatomic gases at low pressure and high temperature