Plate Tectonics Study Guide 1 Provide each student with a hard boiled egg a plate a plastic knife and a napkin 2 Ask students what part of the Earth the eggshell represents 3 Ask students to gently tap the egg on the
1 1 Introduction Plate tectonics is the grand unifying theory in geology It gets that title because many topics in geology can be explained in some way by the movement of tectonic plates Tectonic plates are composed of Earth s crust and the uppermost rigid portion of the mantle Together they are called the lithosphere 1 Similarity of fossils found on continental coasts 2 The close fit of the continental coastlines 3 The matching of glacial grooves on different continents What forms when an oceanic plate is subducted under a continental plate as in a Convergent Plate Boundary An ocean trench and volcanic mountains
Plate Tectonics Study Guide
 Plate Tectonics Study Guide
Plate Tectonics Study Guide
https://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007878905_2-087f8a706ee9a13471410574f78b30a1.png
1 1 Discovering Plate Tectonics As we discovered in the introduction to this lab manual plate tectonics is the model or theory that we use to understand how our planet works More specifically it is a model that explains the origins of continents and oceans folded rocks and mountain ranges igneous and metamorphic rocks earthquakes
Pre-crafted templates provide a time-saving service for creating a varied range of files and files. These pre-designed formats and designs can be utilized for different personal and professional projects, consisting of resumes, invites, leaflets, newsletters, reports, presentations, and more, enhancing the material production procedure.
Plate Tectonics Study Guide

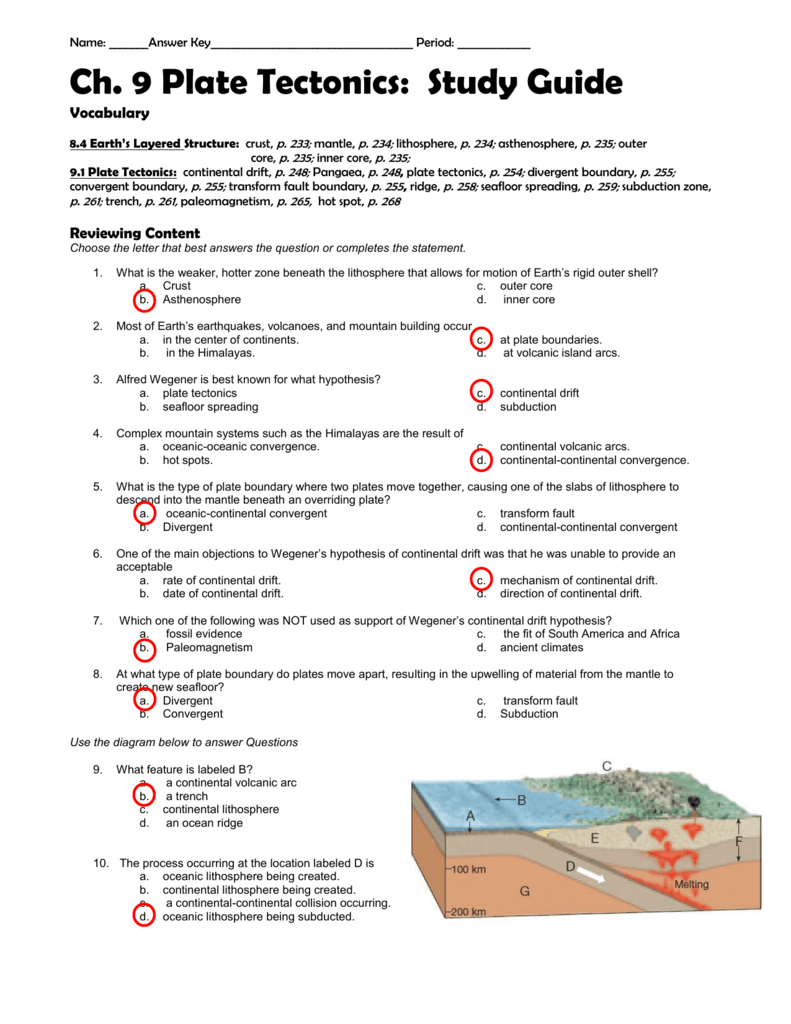
Plate Tectonics Test

Plate Tectonics Unit Test Study Guide

Plate Tectonics Study Guide Ch 4

STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 9 PLATE TECTONICS

Name Pd Plate Tectonics Unit Test Study Guide S6E5a Compare

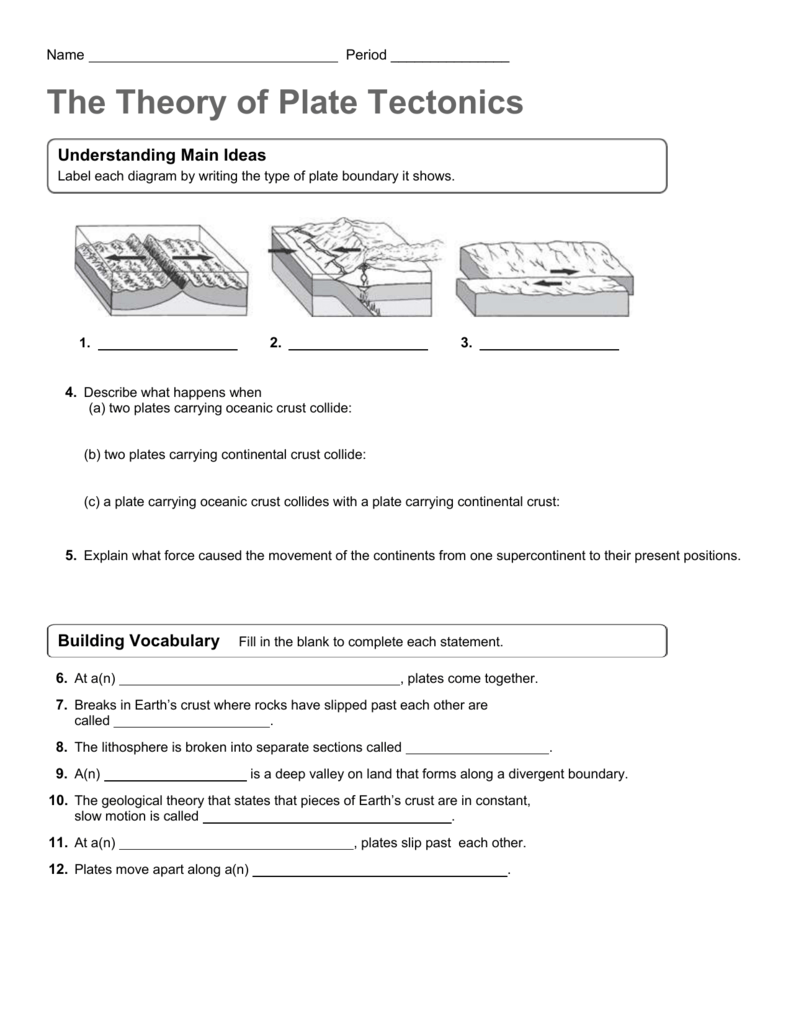
Earth Space Vocabulary Chapter 10 Plate Tectonics The Theory That

http://geoscience.unlv.edu/pub/soukup/Intro_PlateTectonics.pdf
A plate is a rigid slab of rock that moves as a unit As a result the interior of plates tend to be relatively inactive tectonically Plate interiors generally lack earthquakes volcanoes young mountain belts and other evidence of geologic activity

https://www.ck12.org/studyguides/earth-science/earths-tectonic-plates-study-guide.html
Concept Check Define and describe the three types of plate boundaries Explain how plates move Describe where plates are located This study guide summarizes the key points of Earth s Tectonic Plates
https://quizlet.com/164570210/plate-tectonics-study-guide-flash-cards/
The Theory of Plate Tectonics says the crust is split into plates that move around and interact with one another The Theory of Continental Drift says that only the continents are moving We have an expert written solution to this problem
https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/12-001-introduction-to-geology-fall-2013/pages/lecture-notes-and-slides/
Plate Tectonics Lecture 13 15 Notes PDF 1 1MB Lecture 13 15 Slides PDF 9 7MB 17 OJ Continental Crust Formation Notes are not available for this lecture Slides are not available for this lecture 18 OJ Oceanic Crust Formation Notes are not available for this lecture Lecture 18 Slides PDF 4 1MB 19 TP Earthquakes Lecture 19 Notes PDF

https://www.khanacademy.org/science/middle-school-earth-and-space-science/x87d03b443efbea0a:the-geosphere/x87d03b443efbea0a:plate-tectonics/v/introduction-to-plate-tectonics
Introduction to plate tectonics Google Classroom About Transcript Earth s lithosphere is broken up into tectonic plates which move slowly over time Evidence like matching coastlines and same species fossils on different continents support this A plate boundary is where two tectonic plates meet
Plate tectonics states that Earth s surface is made of rigid slabs of rock or plates that move with respect to each other or in relation to each other This new theory suggested that Earth s surface the lithosphere is divided into large pieces of rock These pieces are called plates Each plate moves slowly over Earth s Plates interact in three ways 1 Plates move away from each other at what are called divergent boundaries also known as spreading centers 2 Plates move towards each other at convergent boundaries where continents collide creating mountain ranges or one plate sinks beneath another plate at a subduction zones and can form volcanic arcs 3 P
Theory of Plate Tectonics theory that explains the formation movement of the Earth s crust 3 Lithosphere outermost solid part of the crust solid pieces basalt more dense float 4 Asthenosphere the partially melted part of the mantle that contains convection currents that move the crustal plates