Heat Stake Design Guide Heat Staking Design Guidelines Hollow Stake Works well with Large diameter studs no smaller than 080 O D Produces a large strong head Does not have to melt a large amount of material less time less force Avoids sink marks on the opposite side of molded component
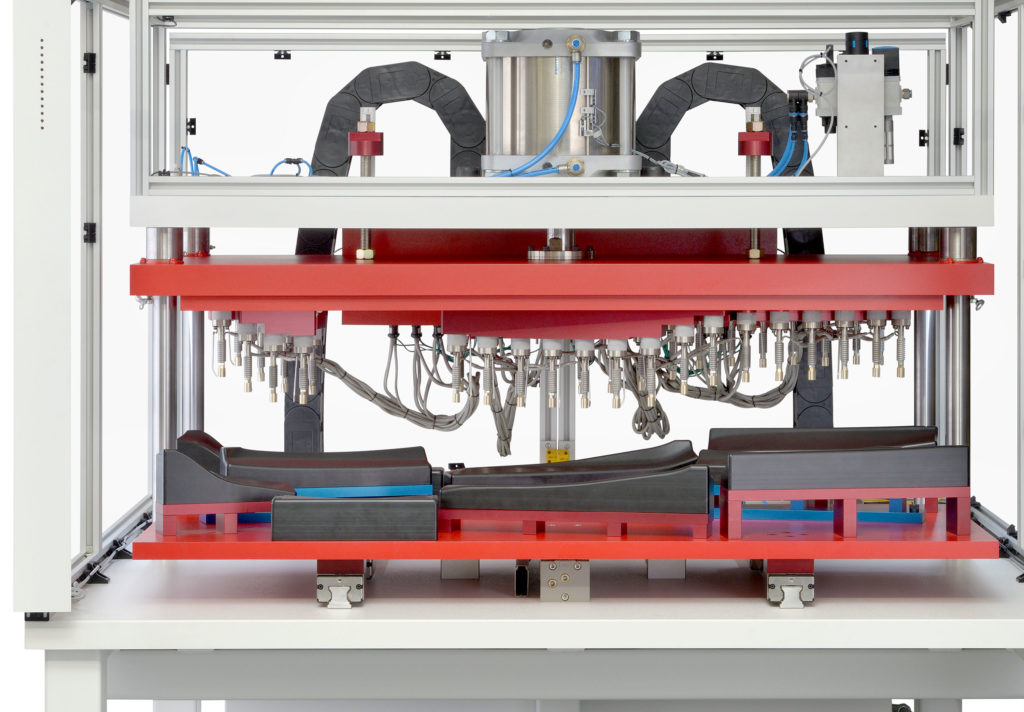
HEAT STAKING DESIGN GUIDELINES Determining The Right Part Joint Design For The Desired Welding Method No matter which plastic assembly operation you choose proper selection and design of component materials i e stakes joints etc are critical to achieve strong fit for purpose welds Heat staking is a process which utilizes pulsed heat to join two or more parts together where at least one part is made out of plastic It works by heating a plastic part to just above the glass transition temperature while simultaneously applying force so that it is deformed The part is then cooled still under force to complete the process
Heat Stake Design Guide
 Heat Stake Design Guide
Heat Stake Design Guide
https://www.heatstaking.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/HS_Slider-1024x712.jpg
How to design for plastic staking Unlock the full potential of your plastic part designs by watching our webinar where industry experts Katherine Urivez and Sean Minch will guide you through cutting edge technologies like InfraStake and nanoSTAKE
Pre-crafted templates provide a time-saving solution for creating a diverse variety of documents and files. These pre-designed formats and layouts can be used for different personal and expert tasks, including resumes, invitations, leaflets, newsletters, reports, discussions, and more, enhancing the content development process.
Heat Stake Design Guide
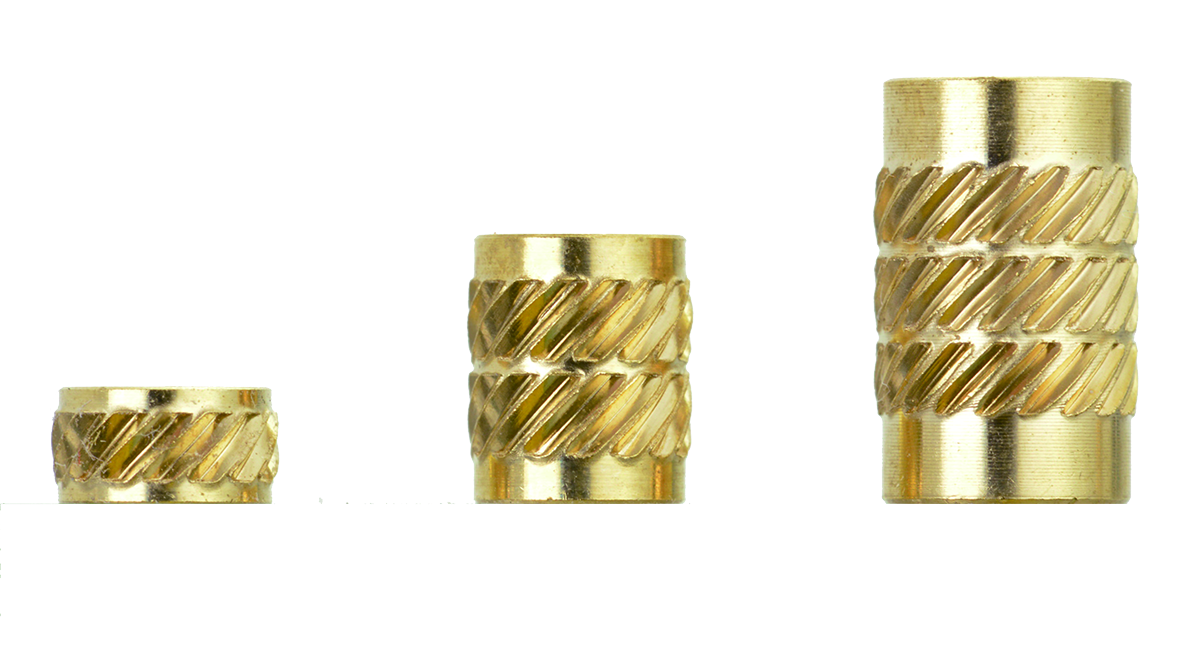
Installation Method Of Insert Nut Heat Staking Inserts

Staking Insertion Why Heat Is The Better Choice Plastics Decorating

Historic Temple Video Series Uintah Stake Tabernacle 1907 3D

Stake Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures

Heat Staking Insert Brass Nut To Plastic YouTube

Billionaire Commodities Dealmaker Squeezed By Rising Rates MINING COM

https://www.amadaweldtech.eu/sites/default/files/documents/whitepapers/AMYE%20Heat%20Stake%20Technical%20document%2003-2016.pdf
Heat Staking is a joining technology to join two or more parts together where at least one is made out of plastic The process is used to melt and deform the plastic material using heat and force at a set process time De forming the plastic is achieved by heating it above the glass transition temperature and apply pressure

https://www.ambrell.com/hubfs/Ambrell_PDFs/411-0172-10.pdf
Introduction Heat Staking Basic Design Guidelines One of the most common uses for induction heating is the heat staking of threaded metal inserts into plastic Most thermoplastics are too soft to sufficiently hold a thread so brass or steel threaded inserts are added

https://www.tomanthermosonics.com/technical-info/thermal-assembly/heat-staking-specs/
Heat staking can be performed using wide range of thermoplastic materials including polypropylene ABS polycarbonate and many others The integrity of a thermal staked assembly depends greatly upon the geometric relationship between the boss and the thermal tip Proper design will produce optimum strength with minimum flash

https://www.ambrell.com/blog/the-new-heat-staking-design-guide
Heat staking of threaded metal inserts into plastic also known as metal to plastic insertion is a common induction heating application and this design guide will help you get started With heat staking the insert is preheated with induction and then pressed into a hole in the plastic part
https://www.heatstaking.com/design-guidelines/
Heat staking is an assembly process that utilizes controlled melting of thermoplastic materials A combination of pressure and heat reform plastic material to join your parts together The results are cosmetically exceptional bonds that are indistinguishable from the original mold
Heat staking systems from bdtronic have a highly developed temperature control that enables processing of these materials as well High performance plastics often have a high melting point or contain various fillers e g glass fibres mineral fibres or aramid fibres All these plastics such as PPS GF65 PPA GF50 PA66 GF50 with a high filler This technical information sheet provides design guidelines congurations and techniques for successful thermal heat staking GENERAL DESCRIPTION Thermal staking is an assembly method that uses the controlled melting and reforming of a plastic stud or boss to capture or lock another plastic or metal component of an assembly in place
Sampling of Insert Design Types Mating Screw Sizes Installation Methods Insert Design Types Insert Materials Finishes Clearance Hole for Ultrasonic Heat Staking Molded in Flange head Symmetrical Full Diamond Knurl Non knurled Symmetrical 2 56 through 5 16 18 and M2 through M8 Aluminum Brass Carbon Steel Stainless Steel Plain Zinc plated